Building Act
| Building Act /Gradbeni Zakon (herein GZ) | National Gazzete of Republic of Slovenia (Nr. 61/17; 02.11.2017) Uradni list RS (št. 61/17; 02.11.2017) |
| Summary | The Building Act regulates the conditions for the construction of facilities and other issues related to the construction of facilities. The purpose of this Act is the protection of the public interest in the construction of facilities. The term public interest includes safety of buildings, respect for the principle of equal opportunities, environmental protection, nature conservation, water protection, protection of cultural heritage, promotion of sustainable construction, compliance of the placement of buildings in the area, architecture as an expression of culture, monitoring, usability, efficiency, quality of facilities and their compliance with the environment through the entire life cycle. The purpose of this Act is realized through design, authorization, construction, use, maintenance and inspection phases of the construction process. The competent authorities in the construction of facilities and all participants in the construction of facilities are obliged to ensure that the requirements referred to in the Building Act are fulfilled within the limits of the rights and obligations laid down by the regulations. |
| Main provisions |
Part 1:
|
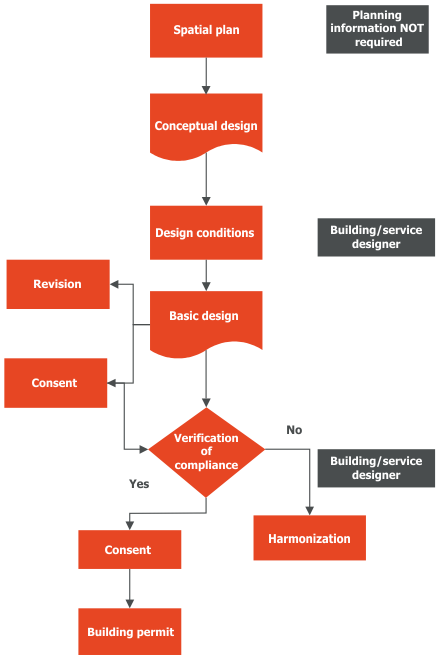
| Information important for WH utilization process (specific information to permissions and documents) |
|
| Link: | Building Act: Gradbeni zakon (GZ) |
Spatial Act
| Spatial Act / Zakon o urejanju prostora (ZUreP-2) | National Gazzete of Republic od Slovenia (Nr. 61/17; 02.11.2017) Uradni list RS (št. 61/17; 02.11.2017) |
| Summary | This legislation defines goals and principles and determines the regulations and rules on spatial planning and management. It defines spatial management measures, instruments and measures of spatial politics, and administers the working of spatial information system and issuing of certificates in the field of spatial planning. |
| Main provisions |
The purpose of Slovenian Spatial Act is to regulate and direct spatial planning to achieve sustainable spatial development with a balanced management of social, environmental and economic factors.
|
| Information important for WH utilization process (specific information to permissions and documents) |
Spatial Act defines spatial regulations, which in turn define the conditions of land’s purpose and use. Waste heat projects will likely need to obtain land for construction of waste heat utilisation premises. The construction of a building (complex or simple) will need to be in accordance with conditions determined under spatial acts for the specific piece of land considered to be used for the project. ZUreP-2 is the legal basis for spatial planning. This includes national, regional and municipal spatial plans. These spatial plans contain information about land use conditions, including whether construction is permitted at a given location and whether any special conditions apply (protected area for nature, water etc.; protection corridors for road, power grids, gas infrastructure etc.). This information is key to establishing whether given location is suitable for waste heat project implementation. Usually the information required for projects will be obtained from local authorities, based on Municipal spatial Plan or Detailed Municipal Spatial Plan. With projects of national significance, the National Spatial Plan will apply. |
| Link: | Spatial Act: Zakon o urejanju prostora (ZUreP-2) |
Architectural and engineering profession Act
| Architectural and engineering profession Act (ZAID) | National Gazzete of Republic od Slovenia (Nr. 61/17; 02.11.2017) Uradni list RS (št. 61/17; 02.11.2017) |
| Summary | This Act defines conditions for the performance of professional tasks related to architecture, engineering, landscape architecture, and spatial planning. The professionals need to be registered with the Chamber of Architecture and Space (ZAPS) and/or Chamber of Engineering of Slovenia (IZS) to gain professional authorization for respective project work. |
| Main provisions | The architectural and engineering profession Act regulates and authorizes 4 key architectural and engineering professions: architects, engineers, spatial planner and landscape architects. Authorized professionals are members of the Architectural and Engineering chamber respectively and are listed on the respective Chamber’s list of professionals. The Act recognizes the competence of authorized professionals and protects it. The Act also contains provisions on duties and responsibilities of listed professions that authorized professionals need to achieve prior to and during their work. |
| Information important for WH utilization process (specific information to permissions and documents) |
Based on the provisions of the Slovenian Building Act, there is a requirement that demanding and less-demanding construction projects need to engage authorised professionals for the development and delivery of building project documentation. This at a minimum includes an authorised architect and authorised engineer, with further professional support as needed depending on the type of the project. |
| Link: | Architectural and engineering profession Act (ZAID) |